Are you in the market for the best generator? You have come to the right place. In this article, we will explore the best generators on the market. Through our comprehensive generator ratings chart, you will be able to quickly and easily compare and contrast the features of the top generators to find the best one for your needs.
Types of Generators
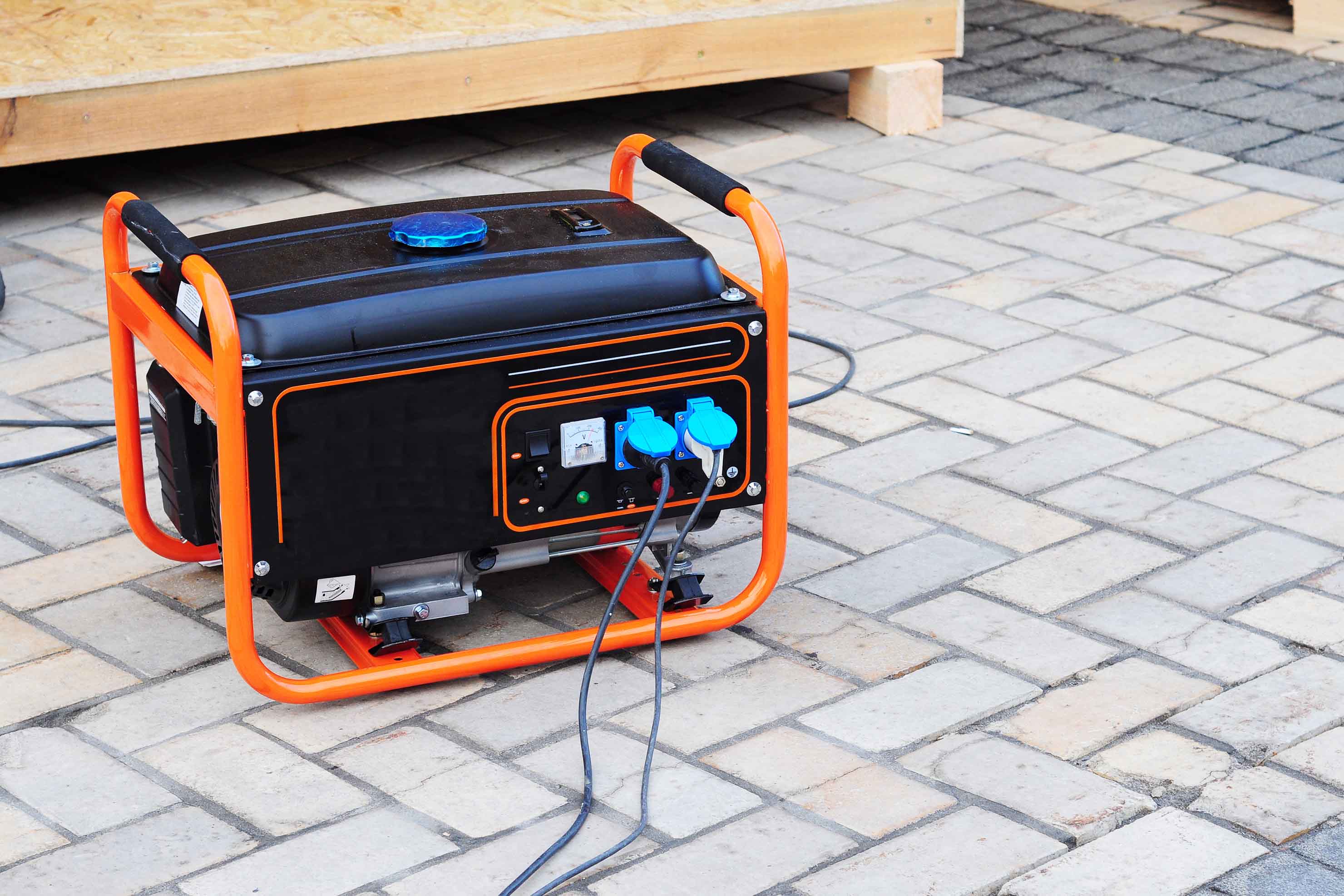

Portable Generators
Portable generators are a versatile choice for homeowners and businesses alike. They are easy to move and can provide power wherever it’s needed. Portable generators are typically powered by gasoline, propane, or diesel and can range in wattage from 2,000 to up to 10,000 or more.
Standby Generators
Standby generators are a great option for those who need reliable power for their home or business. Standby generators are powered by natural gas or propane and are made to be permanently installed outside the home. They are much larger than portable generators and can range in wattage from 6,000 to up to 20,000 or more.
Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are a great option for those who need a portable and reliable source of power. They are powered by gasoline or propane and are designed to be lighter and quieter than traditional portable generators. Inverter generators are typically more expensive than traditional portable generators and can range in wattage from 2,000 to up to 8,000 or more.
Overview

Generators are an important component of any home or business. They provide a reliable source of power in the event of an outage or emergency. Choosing the right generator can be a daunting task, as there are many different types available, each with its own pros and cons. This ratings chart provides an overview of the different types of generators, their ratings, and the features they offer.
Ratings by Type
Portable Generators
Portable generators are a great option for those who need a reliable source of power in a variety of settings. They are typically smaller and lighter than standby generators, making them easy to transport and store. Portable generators are rated according to their power output, which is measured in watts. The higher the wattage, the more powerful the generator is.
Standby Generators
Standby generators are larger, more powerful generators that are typically used in homes and businesses. They are permanently installed and connected to the home’s electrical system, providing a reliable source of power in the event of an outage or emergency. Standby generators are rated according to their power output, which is measured in kilowatts. The higher the kilowatt rating, the more powerful the generator is.
2.3. Inverter Generators


Inverter generators are a newer type of generator in comparison to traditional models. Inverter generators are designed to be lighter, quieter, and more fuel-efficient than traditional generators. They are also equipped with advanced features such as parallel connection capability and digital displays.
Inverter generators are great for camping and RV trips, tailgating, and other outdoor activities. Here are some of the advantages of inverter generators:
- Quiet operation – Most inverter generators are designed to be much quieter than traditional generators.
- Lightweight – Inverter generators are typically much lighter than traditional generators, making them easier to transport and store.
- Fuel-efficiency – Inverter generators are designed to be more fuel-efficient and can run for longer periods of time on the same amount of fuel.
- Parallel connection capability – Some inverter generators have the ability to connect to another inverter generator to increase overall power output.
- Digital displays – Most inverter generators feature a digital display that can show power output, fuel level, and other important information.
Inverter generators are a great option for anyone looking for a reliable, lightweight, and fuel-efficient generator.
3. Factors Affecting Generator Ratings
Generator ratings are an important factor to consider when choosing a generator for your home, business or industrial application. Generator ratings are an indication of the power output of the generator and can vary depending on many different factors. Understanding the factors that influence generator ratings can help you make the right decision for your application.
One key factor that affects generator ratings is the size of the generator. Larger generators have a higher power output, which can help to meet the power needs of an industrial or commercial application. The size of the engine will also have an impact on the generator ratings. Generators with larger engines will have higher power outputs than those with smaller ones.
Another factor that affects generator ratings is the fuel type. Generators that use diesel fuel will typically have higher power outputs than those that use gasoline. Additionally, the type of fuel used can also affect the efficiency of the generator, which can affect the generator ratings.
The type of cooling system used can also have an effect on the generator ratings. Generators with air-cooled systems will typically have lower power outputs than those with liquid-cooled systems. Additionally, the type of cooling system used can affect the efficiency of the generator, which can affect the generator ratings.
The type of generator and the brand can also have an effect on the generator ratings. Generators from reputable brands will typically have higher ratings than those from lesser-known brands. Additionally, the age of the generator can also have an effect on the power output. Older generators may have lower power outputs than newer models.
Finally, the environment in which the generator is used can also have an effect on the power output. Generators used in warmer climates may have lower power outputs than those used in cooler climates. Additionally, generators used in areas with higher altitudes may have lower power outputs than those used in lower altitude areas.
By understanding the factors that affect generator ratings, you can make an informed decision when selecting the right generator for your application. Generators with higher ratings will be able to meet the power needs of larger applications, while those with lower ratings may be better suited for smaller applications.
3.1. Size
Generator size is an important factor to consider when selecting the right model for your needs. In general, larger generators are more powerful and can provide more energy for larger applications. Smaller generators are typically more affordable and can be used for smaller applications, such as camping and home use. Depending on your needs, you may need to consider the size of the generator before making a purchase.
When determining the size of generator you need, you should consider the wattage of the appliances you will be powering. Generally, the higher the wattage, the larger the generator required. It is important to select a generator with a wattage rating that exceeds the wattage of the appliances you plan to use. The wattage rating of a generator is typically listed on the label or in the manual.
In addition to wattage, the physical size of the generator should also be considered. Larger generators tend to be more bulky and require more storage space. On the other hand, smaller generators can be easily stored and transported. The size of a generator can also affect the weight, so be sure to check the weight rating before making a purchase.
Finally, it is important to consider noise levels when selecting the right size generator. Larger generators tend to be louder than their smaller counterparts. If you plan to use the generator in a residential area, you should opt for a model with lower noise levels.
3.2. Power Output


Generators are rated by their power output, which is the maximum amount of electrical energy they can produce. It is typically measured in kilowatts (kW) or megawatts (MW).
The power output of a generator has a direct impact on the types of appliances it can power and the number of appliances it can power at one time. The higher the power output, the more electrical devices can be operated at once.
When selecting a generator, it is important to choose one that has a power output that is suitable for the intended use. Here is a list of common power outputs for generators:
- 1 kW
- 2 kW
- 3 kW
- 4 kW
- 5 kW
- 6 kW
- 7 kW
- 8 kW
- 9 kW
- 10 kW
- 20 kW
- 30 kW
- 40 kW
- 50 kW
- 100 kW
- 150 kW
- 200 kW
- 250 kW
- 300 kW
- 400 kW
- 500 kW
- 600 kW
- 750 kW
- 1 MW
- 2 MW
- 3 MW
- 4 MW
3.3. Fuel Type

Fuel type is an important factor to consider when choosing a generator. Different types of fuel have different characteristics and will affect the performance of the generator. The most common types of fuel used in generators are gasoline, diesel, propane, and natural gas.
Gasoline generators are generally the most affordable option and offer good performance. They are ideal for smaller needs, such as powering a few lights and appliances. However, they are not as efficient as diesel or propane and emit more air pollutants.
Diesel generators are more efficient than gasoline and emit fewer pollutants. They are typically more expensive and require more maintenance, but they provide better performance for larger applications. They are often used for heavy-duty applications such as industrial sites and construction sites.
Propane generators are becoming increasingly popular due to their clean burning characteristics and efficiency. They are typically more expensive than gasoline generators, but offer better performance and are ideal for applications where emissions are a concern.
Natural gas generators are the most efficient type of generator and are the best choice for applications where emissions are a major concern. They are typically more expensive than other types of fuel, but offer better performance and are ideal for larger applications.
Generator Comparison Chart
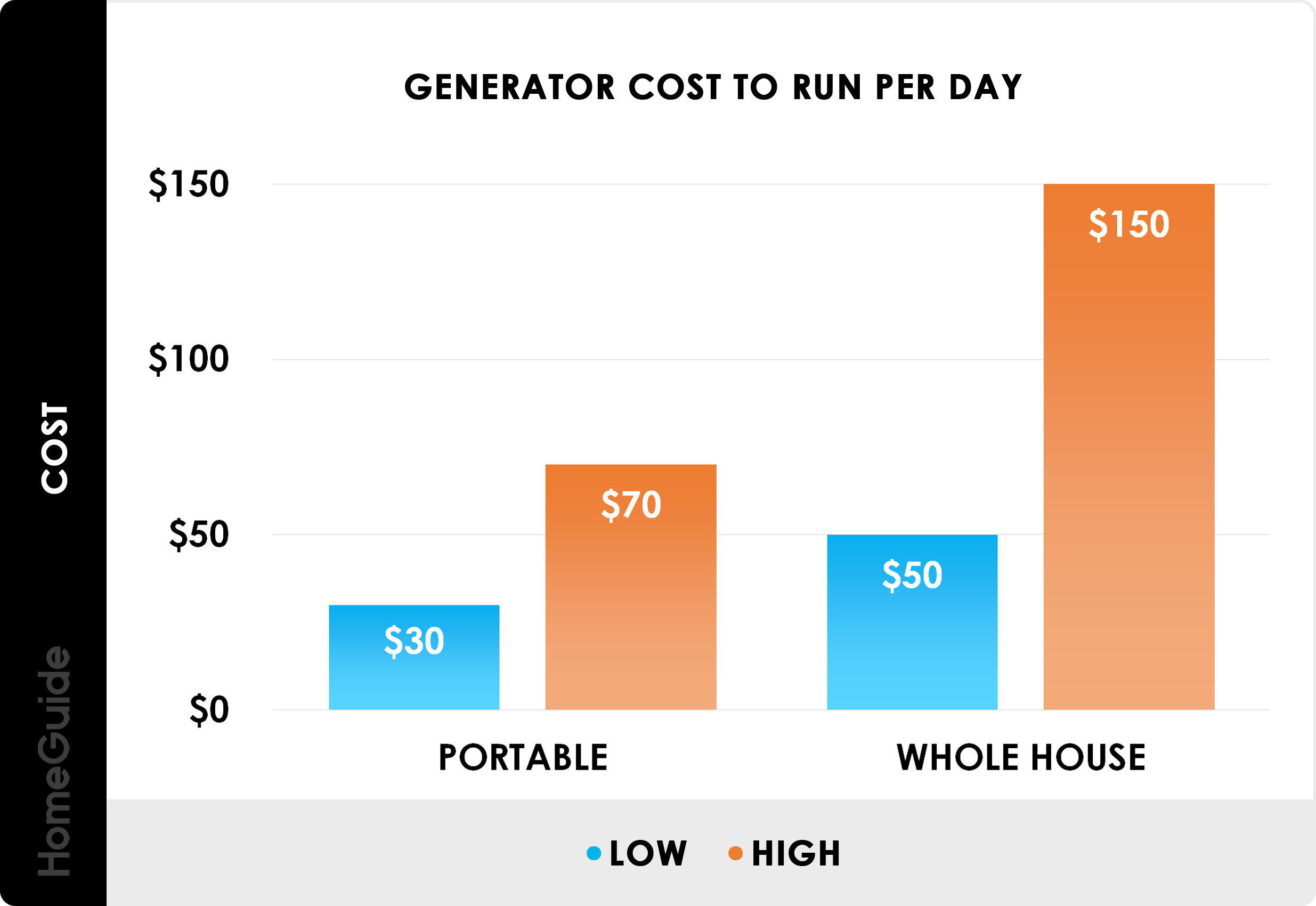
When it comes to choosing a generator, it’s important to understand the different types of generators and their features to ensure you get the best generator for your needs. Below is a generator comparison chart that outlines some of the key features of the various types of generators available on the market.
| Generator Type | Power Output | Portability | Noise Level | Fuel Source | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Generator | Varies, up to 12,000W | Yes, typically with wheels | Generally louder than stationary generators | Gasoline, diesel, propane | $200-$3000 |
| Stationary Generator | Varies, up to 100,000W | No, must be installed | Generally quieter than portable generators | Gasoline, diesel, propane | $1000-$10,000 |
| Solar Generator | Varies, up to 5,000W | Yes, typically with wheels | No noise | Solar | $500-$3000 |
| Wind Generator | Varies, up to 50,000W | No, must be installed | Low noise | Wind | $1000-$30,000 |
When selecting a generator, it is important to evaluate your needs, budget, and preference for portability or size. It is also important to take into account the noise level and fuel source when making a decision. Portable generators are typically less expensive and more versatile, while stationary and wind generators are more powerful but require more installation and maintenance. Solar generators can be a great choice for those looking for clean, renewable energy but have limited space. Ultimately, the generator comparison chart above can help you find the best generator for your needs.
1. Overview

This generator ratings chart is a comprehensive guide to the various types of generators available in the market today. It compares and contrasts the different types of generators, such as portable, standby, and inverter, in terms of their power output, noise level, fuel efficiency, cost, and other important features. This chart also provides ratings and reviews of popular brands, so you can make an informed decision when selecting a generator.
| Features | Portable | Standby | Inverter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Output | Low | High | Low-Medium |
| Noise Level | Medium-High | Low | Low-Medium |
| Fuel Efficiency | Low-Medium | High | High |
| Cost | Lowest | Highest | Medium |
2. Comparisons by Type

When choosing a generator, it is important to understand the differences between types. Here is a comparison chart to help make the decision easier:
| Type | Fuel Source | Noise Level | Power Output | Portability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel | Diesel | Moderate | High | Low |
| Gasoline | Gasoline | Noisy | Moderate | High |
| Propane | Propane | Low | Low | High |
| Natural Gas | Natural Gas | Low | High | Low |
Diesel generators are typically the most powerful, but also the least portable and noisiest. Gasoline generators have an intermediate power output and portability, but are relatively noisy. Propane generators provide good portability but have lower power outputs compared to the other types. Natural gas generators provide the highest power output, but are the least portable.
It is important to consider the pros and cons of each type of generator before making a decision. The chart above provides a useful comparison of the key factors to consider.
2.1. Portable Generators
Portable generators can come in handy for providing temporary power solutions in a range of circumstances. Whether you’re looking for a backup source of electricity for your home, a reliable way to power your RV, or just a way to power up your tools in the garage, a portable generator can be an invaluable piece of equipment.
When selecting a portable generator, it is important to consider the wattage and fuel type. Portable generators can be powered by gasoline, diesel, or propane, and the wattage will determine how much power the generator can supply. The higher the wattage, the more powerful the generator. Depending on the intended use, you may need a generator with a higher wattage to power your larger appliances or tools.
When it comes to noise, the type of generator and wattage you choose will determine how loud it is. Generally speaking, the higher the wattage, the louder the generator. It is important to consider the size of the generator when looking at noise level, as larger generators are typically quieter than smaller ones.
Safety is also an important factor to consider when selecting a generator. Make sure you read the safety warnings and instructions before using the generator. Additionally, be sure to check for any recalls on the brand of generator you choose.
Overall, portable generators can be a great asset for providing temporary power solutions. By considering wattage, fuel type, noise level, and safety, you can select the best generator to meet your needs.
2.2 Standby Generators

Standby generators are used as a form of backup power supply in cases of a power outage. These generators are typically connected to a home or business’s existing electrical system and are designed to kick in automatically when there is an interruption in the main power supply. They are also often referred to as “whole-house” generators as they are capable of powering an entire home or business.
Standby generators come in a variety of sizes, from small portable models to large, commercial-grade units. The size and type of generator you need will depend on your specific power needs and the size of your home or business.
| Rating | Power Output |
|---|---|
| 7 kW | 7,000 watts |
| 10 kW | 10,000 watts |
| 13 kW | 13,000 watts |
| 15 kW | 15,000 watts |
| 20 kW | 20,000 watts |
| 25 kW | 25,000 watts |
| 30 kW | 30,000 watts |
2.3. Inverter Generators


Inverter generators are a relatively new type of generator that have become increasingly popular in recent years. They offer several advantages over traditional generators:
- Inverter generators are much quieter than traditional generators.
- Inverter generators produce cleaner electricity than traditional generators, making them better for sensitive electronics.
- Inverter generators are more fuel-efficient than traditional generators.
- Inverter generators are typically lighter and more portable than traditional generators.
Inverter generators are rated by their wattage output, which can range from 500-5000 watts or higher. They typically cost more than traditional generators, but the higher efficiency and quieter operation makes them a good choice for many types of applications.
3. Factors to Consider

When choosing a generator, it is important to consider a few factors:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Output | The output of the generator should match the power needs of the equipment you plan to use. It is important to consider both the voltage and the wattage of the generator. |
| Noise | Noise levels can vary greatly from generator to generator. If noise is a concern, look for generators that are rated for quiet operation. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Fuel efficiency should be a consideration when selecting a generator. Generators with higher fuel efficiency ratings will save money in the long run. |
| Maintenance | Maintenance requirements can vary from generator to generator. It is important to consider the ease of maintenance when selecting a generator. |
| Price | Price is always a factor when selecting a generator. It is important to consider the cost of the generator as well as the cost of fuel and maintenance. |
These are just a few of the factors to consider when selecting a generator. It is important to consider all of these factors in order to find the best generator for your needs.
3.1. Cost

Generators come in a range of costs. The price of a generator will depend on its size, power, and type. Here is a list of the general cost ranges for different types of generators:
- Portable generators: $500-$2,000
- Inverter generators: $1,000-$4,000
- Standby generators: $2,000-$20,000
- Towable generators: $2,000-$20,000
3.2. Power Output


Generator power output is the measure of the amount of power that a generator can produce. It is typically measured in kilowatts (kW) or megawatts (MW). It is important to note that the rated output of a generator is often different from the actual power output; the rated output is the maximum power that a generator can produce, while the actual power output is the amount of power that is actually produced.
| Generator Rating (kW) | Rated Output (kW) | Actual Output (kW) |
|---|---|---|
| 2.0 | 2.2 | 1.8 |
| 3.0 | 3.3 | 2.7 |
| 4.0 | 4.4 | 3.6 |
| 5.0 | 5.5 | 4.5 |
It is important to note that the rated output of a generator is often different from the actual power output. This can be due to a variety of factors, such as the age of the generator, the type of fuel used, or the environment in which the generator is being used. Different generator manufacturers will have different ratings for the same generator; it is important to consult with the manufacturer to ensure that the generator is rated correctly.
3.3. Noise Level

Noise levels are a critical factor to consider when selecting a generator for your home or business. Generators come in a variety of decibel ratings, ranging from as low as 50 dB to as high as 100 dB.
| Rating | Decibel Level | Noise Level Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent | 50 dB | Quieter than a normal conversation |
| Good | 60 dB | Loud refrigerator |
| Average | 70 dB | Vacuum cleaner |
| Below Average | 80 dB | Lawnmower |
| Poor | 90 dB | Garbage disposal |
| Very Poor | 100 dB | Subway train |
It’s important to note that decibel ratings are logarithmic, meaning that a generator with a decibel rating of 60 dB is twice as loud as one with a rating of 50 dB. When choosing a generator, it’s important to find one that is quiet enough to meet your needs without being a nuisance to those around you.
3.4. Fuel Efficiency
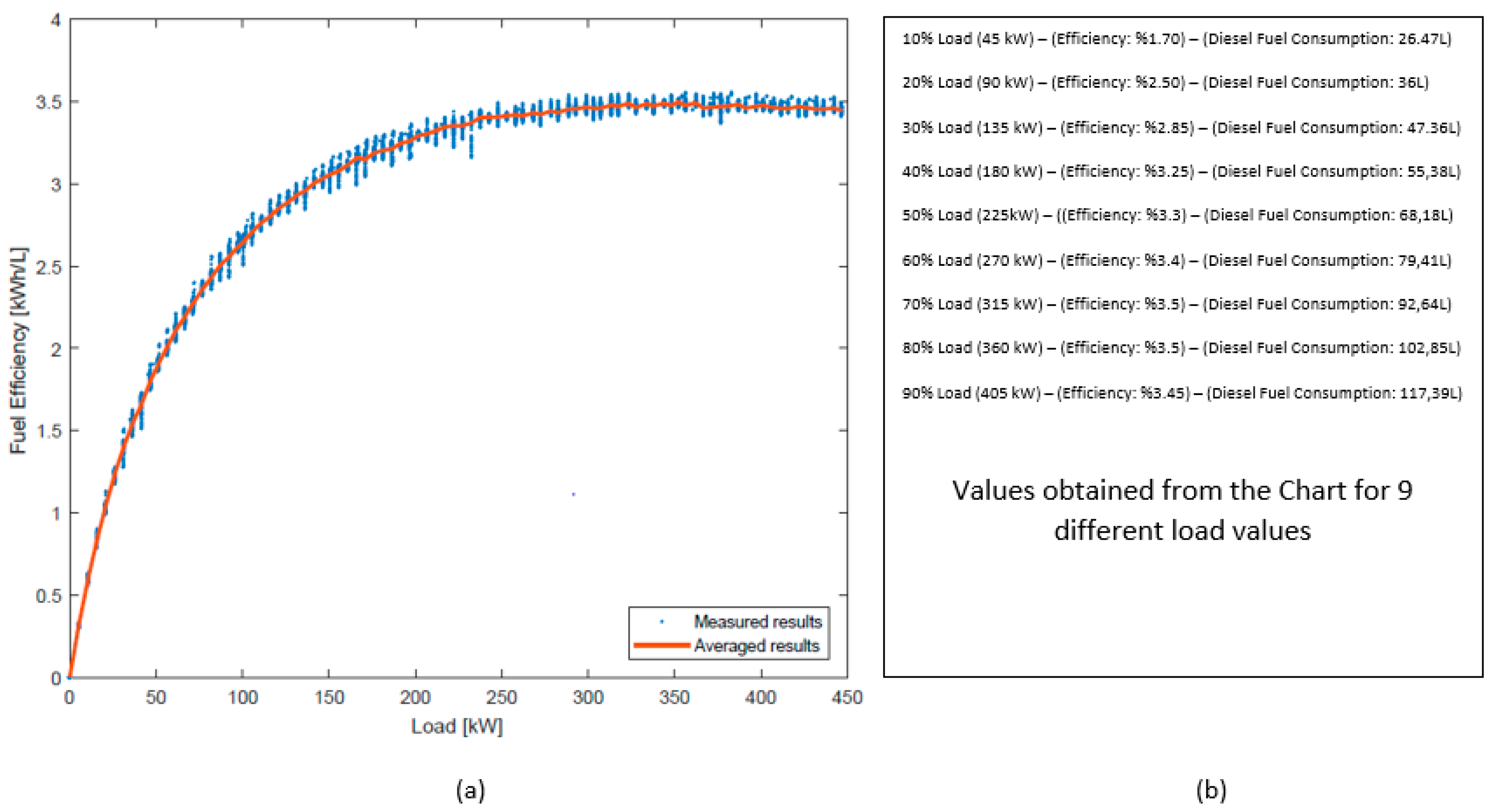
The fuel efficiency of a generator is an important factor to consider when making a purchase. In general, generators with higher fuel efficiency ratings are better for the environment, cost less to run, and produce less noise. Fuel efficiency is measured in gallons per hour (GPH) or liters per hour (LPH).
When looking at a generator’s fuel efficiency rating, consider how frequently the generator will be used. If the generator is only being used occasionally, a higher fuel efficiency rating may not be as important. However, if the generator is being used more often, a higher fuel efficiency rating may be beneficial.
The fuel efficiency of a generator can also vary depending on the type of fuel it uses. Diesel generators typically have higher fuel efficiency ratings. Natural gas and propane generators are also very fuel efficient, while gasoline generators are usually less efficient.
Finally, consider how easy the generator is to maintain. If a generator requires frequent maintenance, it may use more fuel over time. Regular maintenance can help extend the life of the generator and keep it running at its most fuel-efficient level.
3.5. Durability
Durability is a key factor when it comes to evaluating the quality of a generator. If a generator is not durable, it will need to be replaced more often, meaning more money spent in the long run. When looking at generator ratings, durability is usually expressed as the number of hours of operation that the generator can be expected to provide during its lifetime. Generally speaking, the higher the rating, the more durable the generator. Additionally, it is important to look for generators that are made from high-quality materials and have been tested for their durability under various conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an Inverter Generator?
An inverter generator is a type of generator that utilizes an advanced power-management system to produce an AC power source that is extremely clean and stable. Unlike a traditional generator, an inverter generator produces an AC current that is free of voltage spikes and other disruptions that can damage sensitive electrical devices.
Inverter generators are designed to provide a stable power source that is ideal for powering sensitive electronics, such as computers, TVs, and other home electronics. In addition, they are quieter and more fuel-efficient than traditional generators, making them an economical option for both home and camping applications.
Inverter generators offer several advantages over traditional generators, including:
- Quieter operation
- More fuel-efficient
- Produce cleaner, more stable power
- Ideal for powering sensitive electronics
- Lightweight and portable
2. How does a Generator Rating Chart Help Me Choose the Best One?
A generator rating chart can be a great tool to help you make an informed decision when purchasing a generator. It can provide you with valuable information about the different features and capabilities of each generator, allowing you to compare them and decide which is best suited to your needs.
The following points outline how a generator rating chart can help you make a wise choice when it comes to purchasing a generator:
- It can help you determine the size of the generator that you need. This is especially important if you’re looking for a generator to power your home or business, as the size of the generator will determine the amount of power that it can provide.
- It can provide information about the different features of each generator, such as the type of fuel it uses, the noise level it produces, and the runtime it can provide. This can be invaluable in helping you choose the right generator for your needs.
- It can provide you with an overview of the various models of generators available, including their price range. This can be useful in helping you narrow down your search to a few models that fit your budget.
- It can provide information about the warranties offered by the various manufacturers, allowing you to make an informed decision about which generator is right for you.
- Finally, it can give you an idea of how reliable each generator is, allowing you to choose the one that is most likely to provide you with reliable power.
By consulting a generator rating chart, you can make an informed decision about which generator is best for your needs. It can provide you with all the information you need to make a wise decision, ensuring that you get a generator that is reliable, powerful, and within your budget.
3. What are the benefits of a generator comparison chart?
Generator comparison charts are a great way to quickly compare the features, specs, and prices of different generator models. The benefits of using a generator comparison chart are:
- Easy to read and understand: Generator comparison charts are designed to be easy to read, with all the information displayed in a clear and organized manner. This makes it easy to compare and contrast different models side-by-side.
- Time-saving: Rather than having to search through multiple websites and read through product descriptions, a generator comparison chart allows you to quickly view all of the important information about different models in one place.
- In-depth comparison: Generator comparison charts can provide a detailed comparison of different models, including detailed specs, features, and prices.
- Objective comparison: Since all the data is laid out in a standardized format, it’s easier to make an objective comparison between different models.
- Price comparison: Generator comparison charts can also make it easier to compare prices and find the best value for your money.
4. What should I consider when researching generators?
- Type of generator: Portable, standby, inverter, etc.
- Size of generator: kW rating, fuel tank capacity, etc.
- Safety features: Low oil shutdown, GFCI outlets, etc.
- Cost: Initial cost, installation cost, running cost, etc.
- Noise level: dB rating, noise dampening features, etc.
- Durability: Metal or plastic housing, rust protection, etc.
- Ease of use: Digital displays, electric start, remote start, etc.
- Brand reputation: Quality, customer service, warranty, etc.
5. What is the difference between an inverter generator and a regular generator?
Inverter generators and regular generators are both used to produce electricity, but there are several key differences between the two. The main distinction is that an inverter generator produces a cleaner, more stable power than a regular generator. Here are some of the key differences between regular generators and inverter generators:
- Power Output: Regular generators produce electricity at a set speed, usually around 3,600 rpm. This can result in fluctuating power output and can damage certain electronics. Inverter generators, on the other hand, are able to adjust their power output depending on the load, resulting in a more stable and reliable power output.
- Noise Level: Regular generators tend to be much noisier than inverter generators due to the higher rpm they operate at. Inverter generators are much quieter and can produce a noise level as low as 53 dB, which is comparable to the sound of a normal conversation.
- Fuel Efficiency: Regular generators tend to be less fuel-efficient than inverter generators, as they need to run at a constant speed to produce the power output. Inverter generators can adjust their power output and speed to produce the same amount of power while using less fuel.
- Price: Inverter generators are usually more expensive than regular generators. This is mainly due to the higher cost of the components used in the inverter generator, as well as the increased fuel efficiency and quieter operation.
Inverter generators are becoming increasingly popular due to their lower noise levels, fuel efficiency, and stability of power output. While they may be more expensive than regular generators, they can be a great investment if you need a reliable and quiet source of electricity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the best generator for your needs will depend on your individual needs and preferences. It is important to consider the size, power output, fuel type, and other features when making your decision. With the comprehensive generator ratings chart provided above, you can easily compare features and prices between different models to find the perfect generator for your needs. Whether you need a generator for camping, home backup power, or industrial applications, this ratings chart can help you make an informed decision.
References
- Generator Ratings: What You Need to Know Before Buying (2020). Retrieved from https://www.consumerreports.org/generators/generator-ratings-what-you-need-to-know-before-buying/
- Generator Ratings from the Experts at Home Generator Systems (2020). Retrieved from https://homegeneratorsystems.com/generator-ratings/
- Best Generator Reviews 2020: Portable, Standby & Inverter (2020). Retrieved from https://generators.reviewed.com/







